The Rise of Nurabot: AI Robots Stepping In to Alleviate Global Nursing Shortages
The global healthcare sector stands at a critical juncture, grappling with a severe and escalating shortage of nursing professionals. Projections from the World Health Organization (WHO) paint a stark picture, anticipating a deficit of 4.5 million nurses by 2030. This scarcity isn’t merely a future concern; it’s a present crisis. Currently, approximately one-third of nurses worldwide are exhibiting symptoms of burnout, including profound emotional exhaustion, leading to a high turnover rate within the profession. In this challenging landscape, a new contender is emerging: Nurabot, an autonomous, AI-powered nursing robot developed by Taiwanese tech giant Foxconn. This innovative humanoid is designed not to replace nurses, but to serve as a powerful ally, tackling repetitive and physically demanding tasks to significantly reduce their workload.
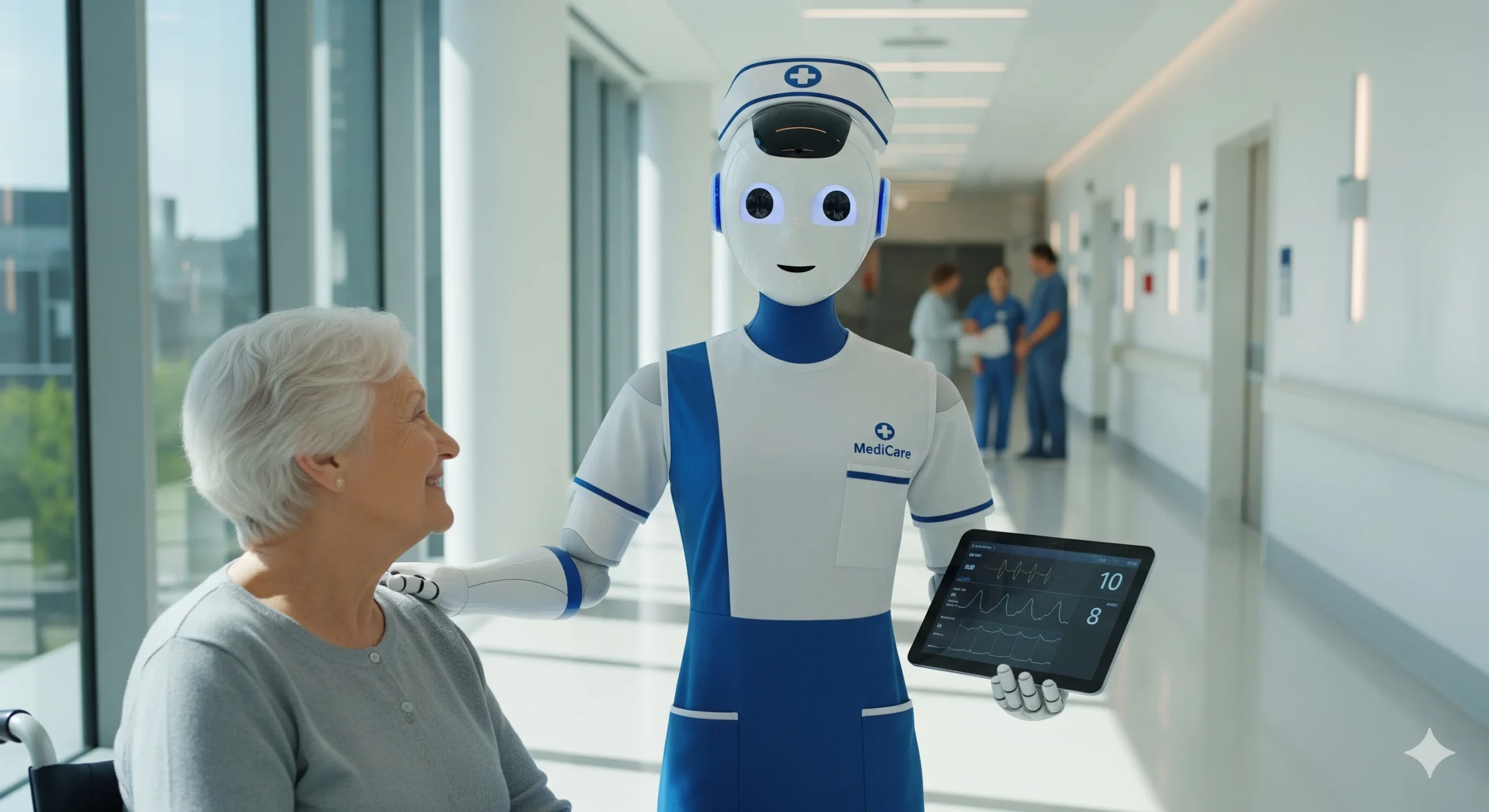

Foxconn, also known as Hon Hai Technology Group, a multinational corporation renowned for its electronics manufacturing, has spearheaded the development of Nurabot. Alice Lin, director of user design at Foxconn, emphasizes that the robot’s purpose is a collaborative mission. “This is not a replacement of nurses, but more like accomplishing a mission together,” she stated. By automating routine duties such as medication delivery and patient escorting, Nurabot aims to free up invaluable nursing time. This allows human healthcare professionals to focus on critical patient care, complex medical judgments, and compassionate interaction, aspects that inherently require human intuition and expertise. Nurabot has been undergoing rigorous pilot testing at Taichung Veterans General Hospital in Taiwan since April 2025, with plans for a commercial launch in early 2026. While a definitive retail price is yet to be announced, the potential impact of such technology on alleviating the strain on healthcare systems is immense.
Technological Foundations: The Fusion of AI and Robotics
The creation of Nurabot is a testament to sophisticated technological collaboration, merging cutting-edge robotics with advanced artificial intelligence. Foxconn partnered with Kawasaki Heavy Industries, a distinguished Japanese robotics company, to engineer the physical architecture of Nurabot. They adapted Kawasaki’s existing “Nyokkey” service robot model, a wheeled autonomous platform equipped with articulated arms capable of lifting and manipulating objects. This base model was enhanced with an array of cameras and sensors, crucial for its ability to perceive and navigate its complex hospital environment.
Foxconn’s development process was deeply informed by extensive research into the daily routines and pain points of nurses. They identified tasks like long-distance travel across wards to deliver samples as significant contributors to workload and potential inefficiencies. To address these, Nurabot was outfitted with specialized compartments designed for the secure and efficient transportation of medications, vials, and other essential supplies. This thoughtful integration of practical needs into the robot’s design highlights a user-centric approach to AI development.
The intelligence powering Nurabot is equally impressive. For its communication capabilities, Foxconn utilized its proprietary Chinese large language model. The core AI and robotics infrastructure was supplied by US tech giant NVIDIA, a leader in artificial intelligence hardware and software. NVIDIA integrated multiple of its advanced AI platforms to enable Nurabot’s sophisticated programming. This allows the robot to autonomously navigate hospital corridors, manage and schedule its tasks, and respond intelligently to both verbal commands and physical cues from staff and patients.
A significant accelerant in Nurabot’s development was the use of AI for virtual training and testing. By creating a digital replica of the hospital environment, engineers could train and refine the robot’s algorithms without the constraints or risks associated with real-world testing. This approach, as David Niewolny, director of business development for health care and medical at NVIDIA, explained, enables Nurabot to “perceive, reason, and act in a more human-like way” and to dynamically adapt its behavior based on the specific patient, context, and situation. This sophisticated blend of hardware and AI is what positions Nurabot as a potentially transformative force in healthcare.
Addressing the Growing Healthcare Crisis: Demographics and Demands
The challenges facing the healthcare industry extend far beyond just nursing shortages. A rapidly aging global population is placing unprecedented demands on healthcare systems. The World Health Organization (WHO) projects a 40% increase in the number of individuals aged 60 and over by 2030, compared to 2019 figures. Projections from the United Nations even suggest that by the mid-2030s, the population aged 80 and older will surpass the number of infants born. This demographic shift means more individuals requiring long-term care and complex medical attention.
While the healthcare workforce has seen steady growth over the past decade, this expansion has not kept pace with the escalating demands driven by population growth and aging. Regions like Southeast Asia are anticipated to be particularly hard-hit by workforce shortages. In such a climate, AI-enhanced systems, like Nurabot, offer a promising avenue for significant time and cost savings. Rick Kwan, a professor of nursing and public health and associate dean at Tung Wah College in Hong Kong, believes that “AI-assisted robots can really replace some repetitive work, and save lots of manpower.” This sentiment underscores the view that AI is not merely a technological novelty but a practical solution to a pressing societal issue. The potential of AI to revolutionize various sectors, from project management to product development, is well-documented, and healthcare is a prime beneficiary of this transformative power. You can explore more about AI for Project Managers and AI Tools for Product Managers to see how AI is reshaping other fields.
However, the integration of robots like Nurabot into healthcare is not without its hurdles. Professor Kwan points to crucial considerations such as patient acceptance of interacting with robots and the necessity for significant infrastructure modifications within hospitals. Many existing hospital facilities, particularly in densely populated urban areas like Hong Kong, feature narrow corridors and are designed primarily around human movement and workflow. This architectural reality poses a challenge for the seamless operation of autonomous robots. A reimagining of hospital design, prioritizing integration with robotic systems, will be essential for widespread adoption.
Furthermore, safety remains a paramount concern. This encompasses not only the mitigation of physical risks associated with robotic operation but also the development of robust ethical guidelines and data protection protocols. Kwan advocates for a gradual and cautious implementation strategy, emphasizing rigorous testing and continuous assessment to ensure both patient well-being and data security. The ethical dimensions of AI, particularly concerning content generation and safety, are complex and require careful navigation, as highlighted in discussions about Grok AI Ethics.
The Evolving Landscape of Healthcare Robotics
Robots are not an entirely new phenomenon in the medical field. Surgical robots, such as the well-established da Vinci system, have been enhancing surgical precision for decades. However, the current wave of innovation is focused on free-moving, humanoids designed to directly assist hospital staff and patients in their daily routines. This represents a significant expansion of robotics from the operating room into the broader hospital environment.
In Singapore, Changi General Hospital is already utilizing over 80 robots to support doctors and nurses with a wide range of tasks, from administrative duties to the delivery of medications. Softbank’s Pepper social bot, for instance, has been deployed in Changi General Hospital to interact with patients, offering a glimpse into the future of human-robot engagement in healthcare.
Across the Pacific, the United States is also seeing widespread adoption of healthcare robots. Nearly 100 “Moxi” autonomous health care bots, developed by Diligent Robots with NVIDIA’s AI platforms, are in operation. These bots are instrumental in transporting medications, laboratory samples, and other essential supplies across hospital wards, mirroring some of Nurabot’s intended functions. The widespread deployment of these robots is indicative of a growing trend towards AI-driven efficiency in healthcare settings. This mirrors the broader impact of AI in business applications, aiming to revolutionize operations and enhance productivity. For insights, explore Top AI Business Applications 2025.
Despite these advancements, comprehensive evidence on the true helpfulness of nursing robots for staff remains an active area of research. A recent review of robots in nursing indicated that while nurses often perceive an increase in efficiency and a reduction in workload, concrete experiential data confirming these benefits is still developing. The review also identified challenges such as technical malfunctions, communication barriers between humans and robots, and the ongoing need for staff training. These findings underscore the importance of thorough testing and user feedback, as exemplified by Nurabot’s pilot program. The integration of AI into various aspects of our lives, from personal devices to complex machinery, is a defining characteristic of this era. For instance, understanding how iPhone AI Battery Optimization works reveals the sophisticated AI embedded in everyday technology.
A Growing Market and the Future of Smart Hospitals
The investment in AI for healthcare is a significant component of the broader $9.8 trillion global healthcare market. Major tech companies, including NVIDIA, Amazon, and Google, are actively exploring new opportunities in this domain. The “smart hospital” sector, a specialized segment of this market, is experiencing rapid expansion. Market research firm Mordor Intelligence projected the smart hospital sector to be valued at $72.24 billion in 2025, with the Asia Pacific region emerging as the fastest-growing market for these innovative solutions. This robust market growth indicates a strong global demand for AI-driven advancements in healthcare.
Nurabot’s current pilot at Taichung Veterans General Hospital in Taiwan is focused on a ward specializing in respiratory and oncological conditions, such as lung cancer and asthma. During this experimental phase, the robot has controlled access to the hospital’s data systems, allowing Foxconn to meticulously “stress test” its functionalities. Key metrics being tracked include the reduction in nurses’ walking distances, the accuracy of deliveries, and qualitative feedback from both patients and nursing staff. Early reports from Foxconn suggest that Nurabot is achieving a reduction in the daily nursing workload of approximately 20–30%. This quantifiable improvement highlights the potential of AI-powered robotics to significantly enhance operational efficiency in healthcare.
While Taichung Veterans General Hospital has not yet officially commented on Nurabot’s performance, Foxconn remains optimistic. According to Alice Lin, Nurabot is slated for formal integration into daily nursing operations later this year, including enhanced connectivity with the hospital information system for autonomous task execution. This integration will precede its commercial launch in early 2026. Lin reiterates that while Nurabot will not entirely solve the fundamental shortage of nurses, it can serve as a crucial tool to “alleviate the problems caused by an aging society, and hospitals losing talent.” This perspective frames AI robots as complementary solutions, augmenting human capabilities rather than replacing them entirely. The broader implications of AI extend to global trade, with the WTO predicting AI could boost global trade by a substantial margin, though with potential risks of increased inequality.
As AI continues its transformative trajectory, its impact on the future of work is a subject of intense discussion. While some foresee shorter workweeks due to increased automation, others are concerned about potential job displacement. The reality is likely to be a complex interplay of both, with new roles emerging and existing ones evolving. For deeper insights into this dynamic, explore articles on AI and the Future of Work and AI Job Shift 2025. The increasing demand for AI-related skills is also reflected in compensation, with reports indicating that AI Jobs Pay 28% More. The rapid advancements in AI technology, such as those seen with DeepSeek’s AI Training Cost, showcase the global race for AI supremacy.



